Building Envelope Mistakes That Lead to Leaks sets the stage for this enthralling narrative, offering readers a glimpse into a story that is rich in detail and brimming with originality. From common errors in building envelopes to the impact of thermal bridging, this guide explores key aspects with a focus on preventing leaks and maintaining structural integrity.
Common Mistakes in Building Envelopes

When it comes to building envelopes, there are several common mistakes that can compromise their integrity and lead to leaks. These mistakes can range from design errors to poor material choices and improper installation, all of which can have a significant impact on the performance of the building envelope.
Design Errors
Design errors in building envelopes can include issues such as inadequate drainage systems, lack of proper flashing details, or improper sealing around openings like windows and doors. These errors can allow water to penetrate the envelope and lead to leaks over time.
For example, if a building does not have sufficient sloping to allow water to drain away from the structure, it can result in standing water that eventually seeps into the building.
Poor Material Choices
The choice of materials used in a building envelope can also contribute to leaks if not selected carefully. For instance, using low-quality sealants or membranes that are not designed for the specific conditions of the building can lead to premature failure and water infiltration.
Inadequate insulation or vapor barriers can also result in moisture problems within the envelope, causing leaks and potential damage to the building.
Improper Installation
Even if the design and materials are sound, improper installation can still compromise the building envelope. Poor workmanship, such as incorrect detailing of joints or seams, can create weak points where water can enter. Improperly installed windows, doors, or cladding can also lead to gaps that allow water penetration.
It is essential to ensure that all components of the building envelope are installed correctly to prevent leaks and maintain the integrity of the structure.
Importance of Proper Flashing and Sealants
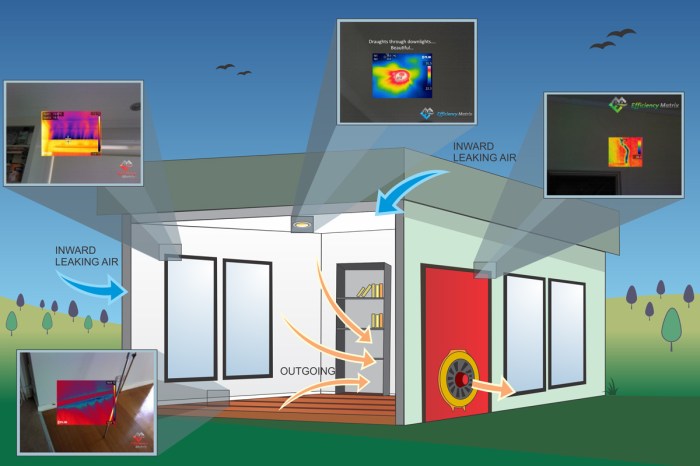
Proper flashing installation and sealants play a crucial role in maintaining the integrity of a building envelope and preventing water leaks.
Role of Correct Flashing Installation
Flashing is essential for directing water away from vulnerable areas of the building envelope, such as windows, doors, and roof joints. It acts as a barrier to prevent water infiltration into the building structure, reducing the risk of moisture-related issues like mold growth and rot.
- Flashing materials like metal, PVC, and rubber are commonly used for different applications based on their durability and flexibility.
- Improper flashing installation, such as gaps or discontinuities, can lead to water seepage and structural damage over time.
- Regular inspection and maintenance of flashing are necessary to ensure its effectiveness in protecting the building envelope.
Role of Sealants in Maintaining a Watertight Envelope
Sealants are used to fill gaps and joints in the building envelope, providing an additional layer of protection against water intrusion. They help create a watertight seal, preventing leaks and air infiltration that can compromise the building's energy efficiency.
- Silicone, polyurethane, and acrylic are common types of sealants used in construction for their adhesive properties and weather resistance.
- Proper application of sealants, including surface preparation and joint design, is essential to ensure their long-term performance.
- Regular inspection and reapplication of sealants are necessary to maintain their effectiveness and prevent water penetration.
Waterproofing Strategies for Building Envelopes

Waterproofing building envelopes is crucial to protect the structure from water damage and infiltration. Proper waterproofing techniques can prevent costly repairs and maintain the integrity of the building over time.
Importance of Drainage Systems
Effective drainage systems are essential in waterproofing building envelopes as they help divert water away from the structure. By directing water away, drainage systems prevent pooling and infiltration that can lead to leaks and damage.
- Install gutters and downspouts to collect and channel rainwater away from the building.
- Ensure proper grading around the foundation to promote water drainage away from the structure.
- Use waterproof membranes and barriers to protect vulnerable areas from water penetration.
Successful Waterproofing Techniques
Industry professionals utilize various successful waterproofing techniques to ensure the building envelope is protected from water intrusion. These techniques have been proven effective in preventing leaks and maintaining the structural integrity of buildings.
- Utilizing high-quality sealants and waterproofing materials on joints and seams.
- Installing flashing around windows, doors, and other openings to prevent water seepage.
- Applying waterproof coatings to exterior walls to create a protective barrier against moisture.
Impact of Thermal Bridging on Building Envelopes
Thermal bridging refers to areas in a building envelope where heat is easily transferred, bypassing insulation and creating pathways for energy loss. This can significantly impact the overall energy efficiency of a building and lead to issues such as condensation and moisture problems.
Implications of Thermal Bridging
Thermal bridging can contribute to condensation and moisture issues within a building envelope. When warm air from the interior of a building comes into contact with a colder surface due to thermal bridging, condensation can form. This moisture buildup can lead to mold growth, reduced indoor air quality, and even structural damage over time.
- Increase in energy consumption due to heat loss
- Decreased comfort levels for occupants
- Potential for structural damage and mold growth
Solutions to mitigate thermal bridging include the use of continuous insulation, thermal breaks, and high-performance windows and doors.
Mitigating Thermal Bridging
To improve energy efficiency and reduce the impact of thermal bridging, several strategies can be implemented. These include:
- Utilizing continuous insulation to minimize heat transfer through the building envelope
- Installing thermal breaks in structural elements to interrupt the flow of heat
- Using high-performance windows and doors with low U-values to reduce thermal bridging
- Implementing air sealing measures to prevent air leakage and heat loss
Outcome Summary
In conclusion, understanding the pitfalls that can compromise a building envelope's effectiveness is crucial in ensuring long-term durability and functionality. By addressing these mistakes proactively, individuals can safeguard their structures against potential water damage and maintain a secure environment for years to come.
FAQ Corner
How do poor material choices affect building envelope integrity?
Poor material choices can compromise the building envelope's ability to resist water penetration, leading to leaks and potential structural damage over time.
What are the key factors to consider in proper flashing installation?
Proper flashing installation involves ensuring a tight seal around openings and transitions to prevent water intrusion, maintaining the building envelope's integrity.
How can thermal bridging impact a building envelope?
Thermal bridging can result in temperature differentials that contribute to condensation and moisture issues, affecting the overall performance of the building envelope.

 When it comes to building envelopes, there are several common mistakes that can compromise their integrity and lead to leaks. These mistakes can range from design errors to poor material choices and improper installation, all of which can have a significant impact on the performance of the building envelope.
When it comes to building envelopes, there are several common mistakes that can compromise their integrity and lead to leaks. These mistakes can range from design errors to poor material choices and improper installation, all of which can have a significant impact on the performance of the building envelope.
 Proper flashing installation and sealants play a crucial role in maintaining the integrity of a building envelope and preventing water leaks.
Proper flashing installation and sealants play a crucial role in maintaining the integrity of a building envelope and preventing water leaks.
 Waterproofing building envelopes is crucial to protect the structure from water damage and infiltration. Proper waterproofing techniques can prevent costly repairs and maintain the integrity of the building over time.
Waterproofing building envelopes is crucial to protect the structure from water damage and infiltration. Proper waterproofing techniques can prevent costly repairs and maintain the integrity of the building over time.












